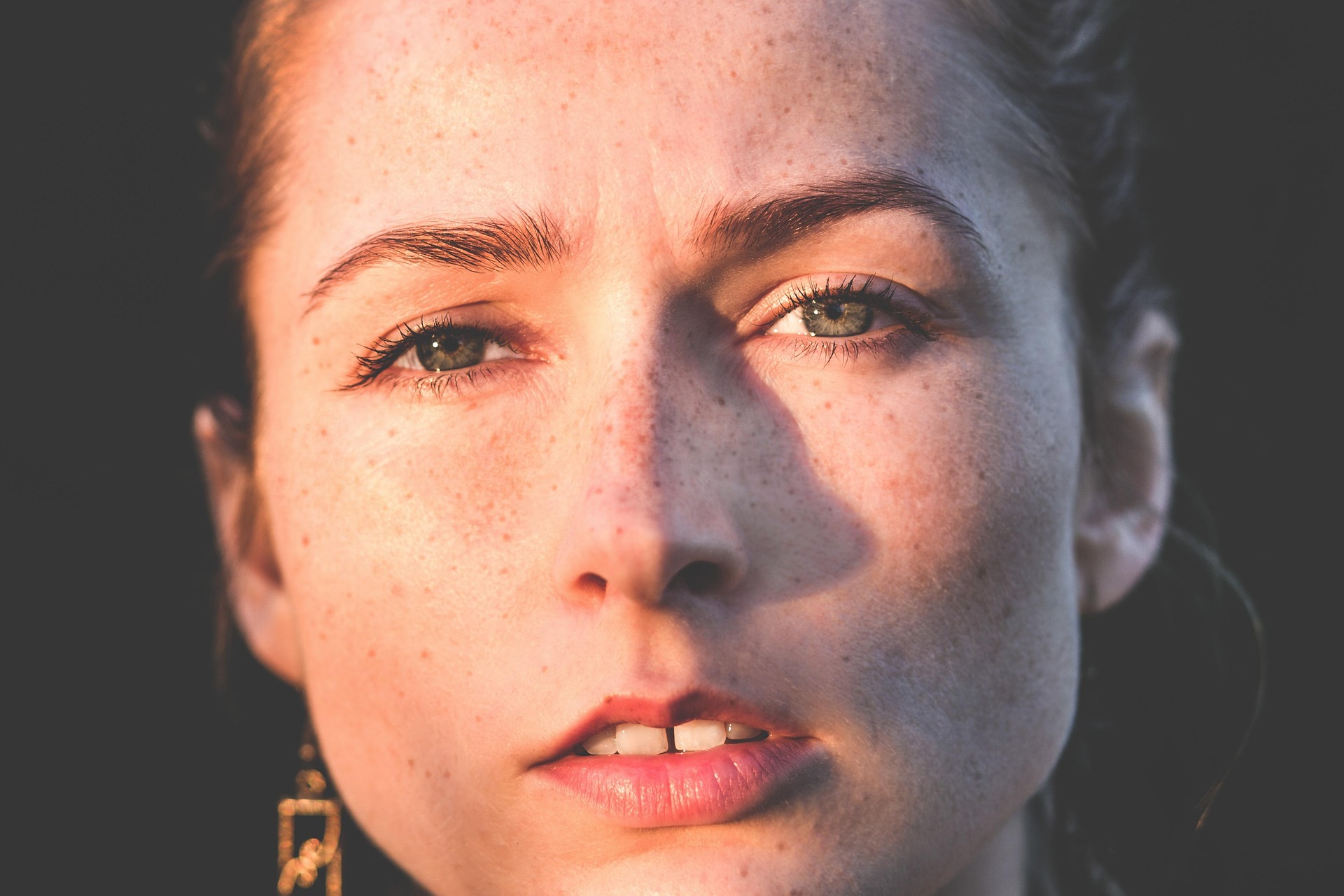
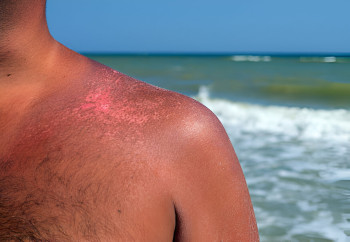
Hyperpigmentation refers to dark patches of skin caused by excess melanin production. It can result from sun damage, acne scars, hormonal changes, or injury.
Common Types
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): After acne or injury
Melasma: Often hormone-related, appears on cheeks and forehead
Sunspots: Result from prolonged UV exposure
Causes
Sun exposure
Hormonal fluctuations (e.g., pregnancy)
Inflammation from acne or eczema
Skin trauma (burns, cuts, etc.)
Effective Treatments
Topical Ingredients: Vitamin C, niacinamide, kojic acid, azelaic acid
Chemical Peels: Exfoliate top layers to reveal clearer skin
Laser Therapy: Targets pigment and breaks it down
Microneedling: Stimulates collagen and reduces dark spots over time
Prevention Tips
Daily SPF use
Avoid picking at the skin
Use gentle products to prevent inflammation
Conclusion Consistency is key. Treating hyperpigmentation takes time, but with the right routine and expert guidance, significant improvement is possible.